Linux 编程指南
GPIO 应用编程
C参考代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <string.h> static char gpio_path[100]; //设置GPIO方向、高低电平 static int gpio_config(const char *file, const char *value) { char config_path[100]; int len; int fd; sprintf(config_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, file); if (0 > (fd = open(config_path, O_WRONLY))) { perror("open error"); return fd; } len = strlen(value); if (len != write(fd, value, len)) { perror("write error"); close(fd); return -1; } close(fd); return 0; } //获取GPIO的方向、电平 static int gpio_get(const char *file) { char get_path[100]; char buf[10]={"\0"}; int len; int fd; sprintf(get_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, file); if (0 > (fd = open(get_path, O_RDWR))) { perror("open error"); return fd; } if ( 0 > read(fd,buf,10)) { perror("read error"); return fd; } printf(" %s : %s",file,buf); close(fd); return 0; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (4 != argc) { if (3 != argc) { fprintf(stderr, "set gpio out : %s <gpio> <out> <value>\n", argv[0]); fprintf(stderr, "set gpio in : %s <gpio> <in>\n", argv[0]); exit(-1); } } sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]); if (access(gpio_path, F_OK)) { printf("%s inexistence,export %s... \n",gpio_path,argv[1]); int fd; int len; if (0 > (fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY))) { perror("open error"); exit(-1); } len = strlen(argv[1]); if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len)) { perror("write error"); close(fd); exit(-1); } close(fd); } if (gpio_config("direction", argv[2])) exit(-1); if ( 0 == strcmp("out",argv[2] ) && argc == 4 ) { if(gpio_config("value", argv[3])) exit(-1); } printf("GPIO%s:\n",argv[1]); if (gpio_get("direction")) exit(-1); if (gpio_get("value")) exit(-1); exit(0); }
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o gpio gpio.c
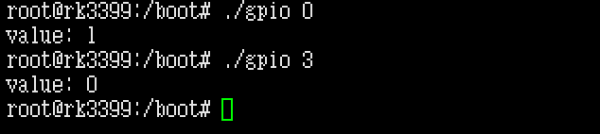
将编译好的gpio程序使用scp拷贝到 r39s2 主板上,执行测试:
使用方法:
0:./gpio 3
1:./gpio 1
UART 应用编程
系统下操作 UART 的测试串口,以 J_RS232 TX3\RX3 测试为例:
J_RS232 TX3\RX3 设备节点为:
/dev/ttysWK2
C参考UART高低电平输入代码如下:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <termios.h> #include <errno.h> int set_opt(int,int,int,char,int); void main(){ int fd,nByte; char *uart3 = "/dev/ttyS2"; char bufferR[2]; char bufferW[2]; memset(bufferR, '\0', 2); memset(bufferW, '\0', 2); if((fd=open(uart3,O_RDWR,0777))<0) { printf("failed\n"); } else{ printf("success\n"); set_opt(fd, 115200, 8, 'N', 1); } while(1){ nByte = 0; memset(bufferR, '\0', 2); memset(bufferW, '\0', 2); // printf("hello\n"); if((nByte = read(fd, bufferR, 1)) == 1){ //MCU串口发送接收都是单字节(单字符)函数 printf("receive:%c\n",bufferR[0]); bufferW[0] = 'A'; write(fd,bufferW,1); //串口发送单字节(单字符) buffer[0] = data memset(bufferR, '\0', 2); memset(bufferW, '\0', 2); nByte = 0; } } close(fd); } //串口通用初始化函数 int set_opt(int fd,int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop) { struct termios newtio,oldtio;//定义结构体newtio和oldtio //将原串口的数据取到oldtio if ( tcgetattr( fd,&oldtio) != 0) { perror("SetupSerial 1"); return -1; } //将newio清零和设置c_cflag bzero( &newtio, sizeof( newtio ) ); newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL | CREAD;//使能接收和忽略控制线 newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE; //设置数据位 switch( nBits ) { case 7: newtio.c_cflag |= CS7; break; case 8: newtio.c_cflag |= CS8; break; } //设置校验位 switch( nEvent ) { //偶校验 case 'O': newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;//使能奇偶校验 newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD;//偶校验 newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);//输入校验并忽略第八位 break; case 'E': newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP); newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB; newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;//取消偶校验(置零偶校验位),开启奇校验 break; case 'N': newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;//不进行奇偶校验 break; } //设置波特率 switch( nSpeed ) { case 2400: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400); break; case 4800: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800); break; case 9600: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600); break; case 115200: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200); break; case 460800: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B460800); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B460800); break; default: cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600); cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600); break; } //设置停止位 if( nStop == 1 ) newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;//一位停止位 else if ( nStop == 2 ) newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;//两位停止位 newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;//不设置读取超时 newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;//读取最小字符数为0 tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH);//清空缓冲区 //使配置生效 if((tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&newtio))!=0) { perror("com set error"); return -1; } // printf("set done!\n\r"); return 0; }
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o uart uart.c
将编译好的程序使用 scp 拷贝到 3399 主板上,执行测试:
KEY 应用编程
参考系统下操作Key的方法,获取到key的设备节点为
/dev/input/event2
C参考代码如下:
#include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <linux/input.h> #include <sys/select.h> #define INPUT_DEVICE "/dev/input/event2" int main(int argc, char **argv){ int fd; struct input_event event; ssize_t bytesRead; int ret; fd_set readfds; if ( 0 > (fd = open(INPUT_DEVICE,O_RDONLY))) { perror("open error"); return fd; } while(1){ FD_ZERO(&readfds); FD_SET(fd,&readfds); ret = select(fd + 1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, NULL); if (ret == -1){ fprintf(stderr,"select call on%s : an error ocurred",argv[1]); break; } if(FD_ISSET(fd,&readfds)){ bytesRead = read(fd, &event,sizeof(struct input_event)); if(bytesRead == -1 ) fprintf(stderr,"bytesRead :%ld : an error ocurred",bytesRead); } if(event.type == EV_KEY && (event.value == 0 || event.value == 1)) { printf("key %s\n",(event.value) ? "pressed" : "released"); } } close(fd); return EXIT_SUCCESS; }
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o key key.c
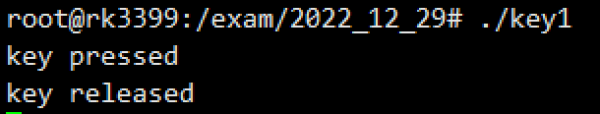
将编译好的程序使用 scp 拷贝到 r39s2 主板上,执行测试,按动 key 打印如下:
- 按下按键时显示:key pressed
- 松开按键时显示:key released