这是本文档旧的修订版!
目录
}
资源特性
}
接口布局和尺寸
快速上手
系统下载
Linux系统
Buildroot:
工具链下载
工具
烧录工具下载
烧录工具
系统烧录
1、下载烧录工具:
2、开始烧录:
3、完成烧录:
- 烧录过程不需要任何操作,烧录成功后右框会显示设备自动重启,烧录完成。
串口调试
- Windows 上一般用 putty 或 SecureCRT。以 putty 为例介绍如何使用串口调试功能
- putty下载链接:下载链接,选择putty.exe
- 串口通讯参数配置:
波特率:115200 数据位:8 停止位:1 奇偶校验:无 流控:无
- putty设置界面如下:
1.Connection type设置为Serial 2.Serial line设置为pc端连接的串口(此项填写pc端实际的串口号) 3.Speed设置为150000 4.点击Open按钮打开终端
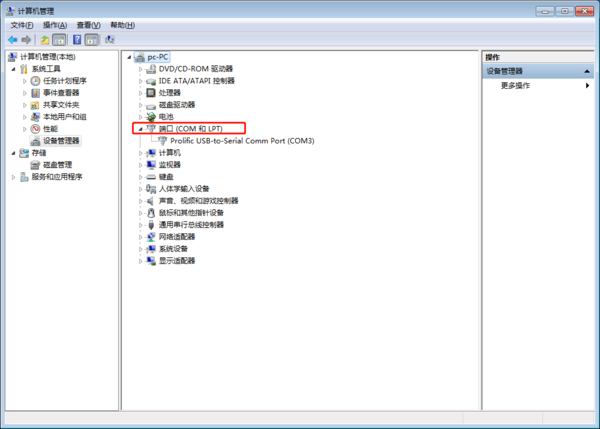
- 查看PC端的串口号:
- 右键点击我的电脑->管理->设备管理器->端口(COM和LPT)找到本机对应的串口
- 如无设备请先确定pc端是否自带串口及驱动是否安装
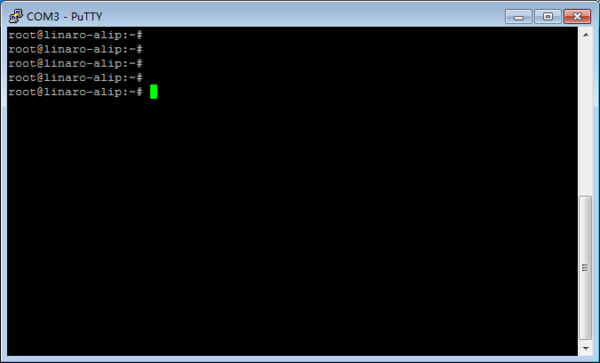
- 进入串口调试终端:
- 如图进入交互界面,敲击回车或者输入命令会有反馈
ssh连接
网络接口IP地址默认设置如下:
ECAT : dhcp (1000M)
LAN2 : 192.168.1.10 (100M)
LAN3 : 192.168.10.10 (100M)
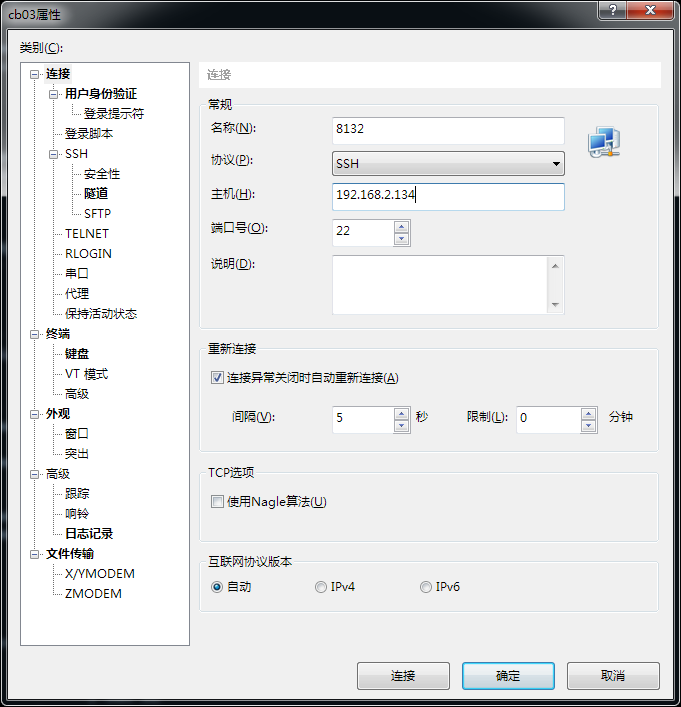
打开xshell,新建连接,输入IP地址:
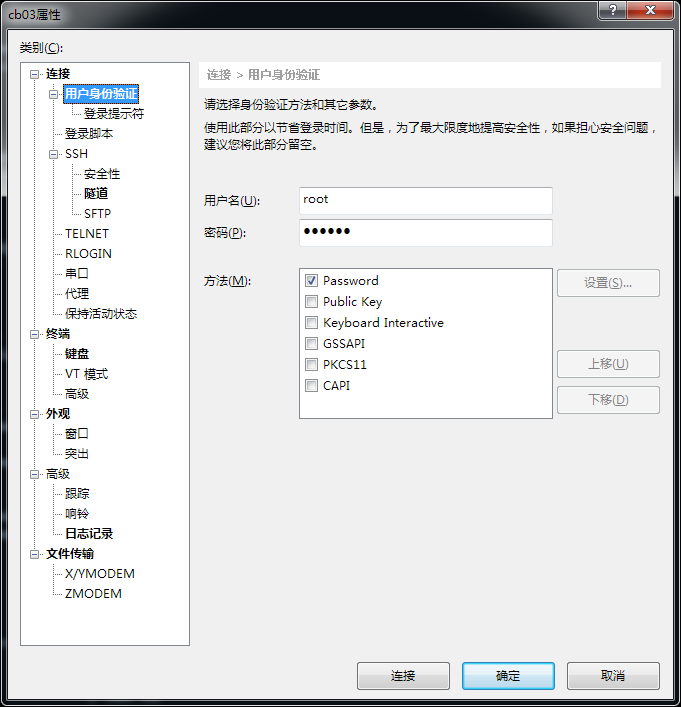
用户身份验证
用户名为:root 密码为为: 123456
点击连接,提示ssh密钥认证:
Linux系统的使用
以太网使用方法
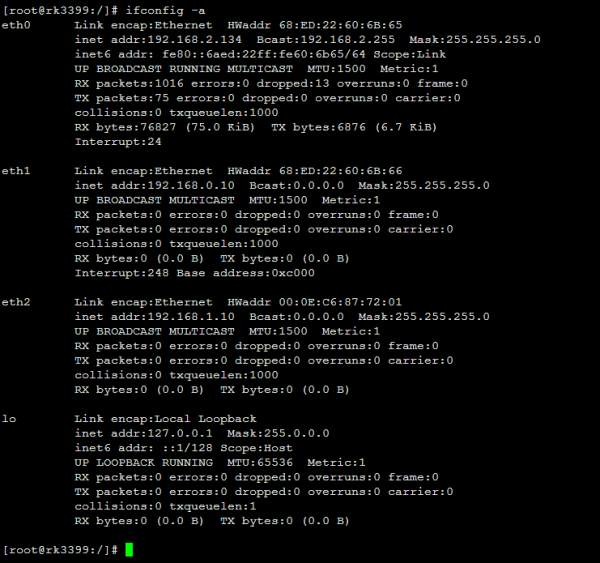
查看所有网络设备
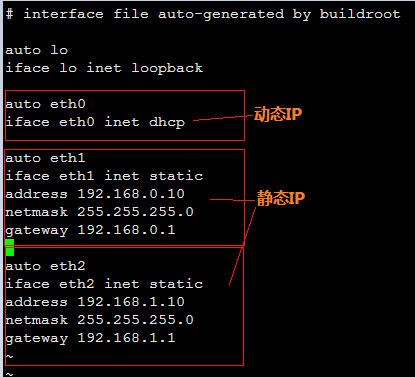
设置静态IP与动态IP
设置DNS
# vi /etc/resolv.conf
Ping测试
# ping 192.168.2.238 -s 65000 //指定数据包大小 # ping 192.168.2.238 -c 10 //指定ping次数
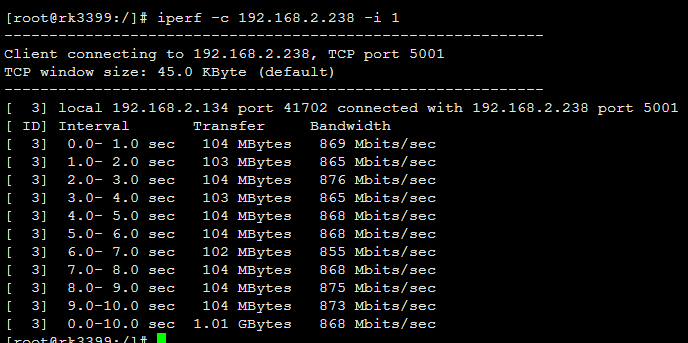
Iperf Throughput 测试
需要与server端配合使用, server端需要安装iperf测试工具 在server端开启iperf: $ iperf -s 在测试端开启iperf测试: # iperf -c 192.168.2.238 -i 1 //192.168.2.238 为server端IP地址
串口使用方法
RS485
对应设备节点: 485A1/B1 -- /dev/ttyS2 485A2/B2 -- /dev/ttyS3
测试方法 硬件连接:将485A1/B1 对接 485A2/B2: 设置串口:
使用485A1/B1接收:
com_recv /dev/ttyS2 115200
使用485A2/B2发送
com_send /dev/ttyS3 115200
{{:pasted:20230813-225324.png}}
RS232
对应设备节点: RS232RX/TX -- /dev/ttyS4
测试方法 硬件连接:将RX/TX短接: 接收:
com_recv /dev/ttyS4 115200
发送:
com_send /dev/ttyS4 115200
在接收端可以收到字符:
CANBUS使用方法
CAN接口定义
CAN测试方法,连接CAN1L – CAN2L ,CAN1H – CAN2H 设置can:
ip link set can0 down ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 ip link set can0 up
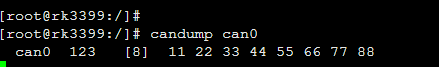
使用can0 接收:
candump can0
使用can1发送数据帧:
cansend can1 123#1122334455667788
查看接收端:
C编程指导参考:CAN应用编程
左右拨码开关使用方法
WATCHDOG使用方法
设置看门狗timeout超时时间
i2ctransfer -y -f 4 w3@0x15 0x00 0x02 0x01 (1分钟)
以此类比 0x01=1分钟 0x02=2分钟 0x03=3分钟
打开watchdog
i2ctransfer -y -f 4 w3@0x15 0x00 0x03 0x01
喂狗:
i2ctransfer -y -f 4 w3@0x15 0x00 0x04 0x01
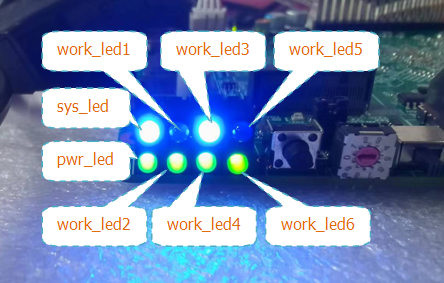
LED使用方法
系统共有8个LED,pwr_led不可以控制其中7个LED均可控,系统下对应的设备接口为:
[root@rk3399:~]# cd /sys/class/leds/ [root@rk3399:/sys/class/leds]# ls mmc1:: sys_led work_led1 work_led2 work_led3 work_led4 work_led5 work_led6
控制work_led1熄灭
echo 0 >/sys/class/leds/work_led1/brightness
控制work_led1点亮
echo 1 >/sys/class/leds/work_led1/brightness
其他LED类似
RTC使用方法
查看当前系统时间:
[root@rk3399:~]# date Wed Jun 8 15:54:09 CST 2022
设置同步硬件时钟:
[root@rk3399:/]# date -s "2022-06-08 17:01:01" Wed Jun 8 17:01:01 CST 2022 [root@rk3399:/]# hwclock -w [root@rk3399:/]# hwclock -r Wed Jun 8 17:01:09 2022 0.000000 seconds
关机断电5秒以上,再开机查看系统时间是否保存:
[root@rk3399:/]# date Wed Jun 8 17:02:30 CST 2022
TFCARD使用方法
接入TFCARD,如果TFCARD有分区,系统会自动挂载到/mnt/sdcard
[root@rk3399:/]# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/root 14781436 480548 13675260 4% / devtmpfs 1962984 0 1962984 0% /dev tmpfs 1963920 28 1963892 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 1963920 176 1963744 1% /tmp tmpfs 1963920 304 1963616 1% /run /dev/mmcblk0p6 3462176 2768616 497976 85% /mnt/sdcard
十段位编码开关使用方法
扩展IO卡使用方法
USB接口使用
系统支持U盘自动挂载:/media/usb0
[root@rk3399:/]# df Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on /dev/root 14781436 480556 13675252 4% / devtmpfs 1962984 0 1962984 0% /dev tmpfs 1963920 28 1963892 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 1963920 184 1963736 1% /tmp tmpfs 1963920 288 1963632 1% /run /dev/sda1 1046512 2728 1043784 1% /media/usb0
Linux C编程指导
交叉编译环境
1. 建议主机环境:
Ubuntu 18.04 x86_64
2. 下载安装交叉编译工具链:
apt install -y crossbuild-essential-arm64
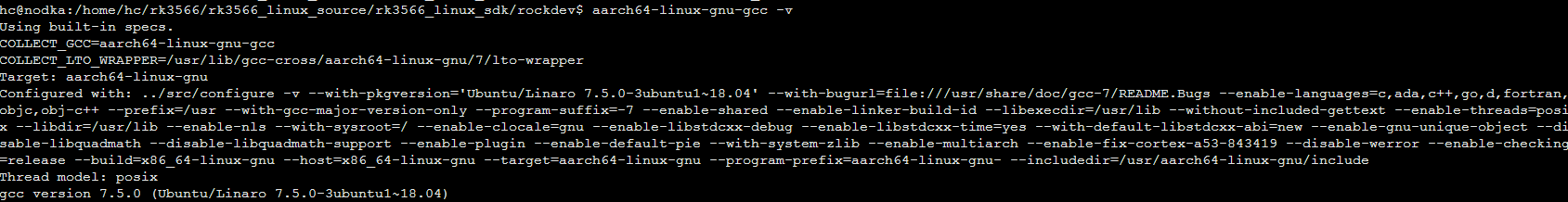
3. 查看是否安装正确:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -v
系统有打印Gcc 版本即为正常:
GPIO应用编程
系统下操作GPIO的方式参考IO使用方法
C参考代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
static char gpio_path[100];
//设置GPIO方向、高低电平
static int gpio_config(const char *file, const char *value)
{
char config_path[100];
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(config_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, file);
if (0 > (fd = open(config_path, O_WRONLY)))
{
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
len = strlen(value);
if (len != write(fd, value, len))
{
perror("write error");
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
//获取GPIO的方向、电平
static int gpio_get(const char *file)
{
char get_path[100];
char buf[10]={"\0"};
int len;
int fd;
sprintf(get_path, "%s/%s", gpio_path, file);
if (0 > (fd = open(get_path, O_RDWR)))
{
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
if ( 0 > read(fd,buf,10))
{
perror("read error");
return fd;
}
printf(" %s : %s",file,buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (4 != argc)
{
if (3 != argc)
{
fprintf(stderr, "set gpio out : %s <gpio> <out> <value>\n", argv[0]);
fprintf(stderr, "set gpio in : %s <gpio> <in>\n", argv[0]);
exit(-1);
}
}
sprintf(gpio_path, "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%s", argv[1]);
if (access(gpio_path, F_OK))
{
printf("%s inexistence,export %s... \n",gpio_path,argv[1]);
int fd;
int len;
if (0 > (fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY)))
{
perror("open error"); exit(-1);
}
len = strlen(argv[1]);
if (len != write(fd, argv[1], len))
{
perror("write error");
close(fd);
exit(-1);
}
close(fd);
}
if (gpio_config("direction", argv[2]))
exit(-1);
if ( 0 == strcmp("out",argv[2] ) && argc == 4 )
{
if(gpio_config("value", argv[3]))
exit(-1);
}
printf("GPIO%s:\n",argv[1]);
if (gpio_get("direction"))
exit(-1);
if (gpio_get("value"))
exit(-1);
exit(0);
}
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o gpio gpio.c
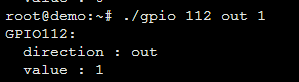
将编译好的gpio程序使用scp 拷贝到8132 主板上,执行测试:
使用方法:
set gpio out : ./gpio <gpio> <out> <value> set gpio in : ./gpio <gpio> <in>
Switch应用编程
参考系统下操作Switch的方法:左右拨码开关使用方法,获取到switch的设备节点为
/dev/input/event2
C参考代码如下:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#define INPUT_DEVICE "/dev/input/event2"
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int fd;
struct input_event event;
ssize_t bytesRead;
int ret;
fd_set readfds;
if ( 0 > (fd = open(INPUT_DEVICE,O_RDONLY)))
{
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
while(1){
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
FD_SET(fd,&readfds);
ret = select(fd + 1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (ret == -1){
fprintf(stderr,"select call on%s : an error ocurred",argv[1]);
break;
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&readfds)){
bytesRead = read(fd, &event,sizeof(struct input_event));
if(bytesRead == -1 )
fprintf(stderr,"bytesRead :%ld : an error ocurred",bytesRead);
}
if (event.type == EV_KEY && event.code == KEY_RIGHT){
if(event.value == 1)
printf("Switch on the right\n");
}
if (event.type == EV_KEY && event.code == KEY_LEFT){
if(event.value == 1)
printf("Switch on the left\n");
}
}
close(fd);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o switch switch.c
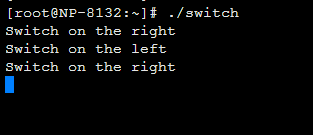
将编译好的程序使用scp 拷贝到8132 主板上,执行测试,拨动switch打印如下:
Rotary应用编程
参考系统下操作Rotary的方法:编码开关使用方法,获取到Rotary的设备节点为
/dev/input/event1
C参考代码如下:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#define INPUT_DEVICE "/dev/input/event1"
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int fd;
struct input_event event;
ssize_t bytesRead;
int ret;
fd_set readfds;
if ( 0 > (fd = open(INPUT_DEVICE,O_RDONLY)))
{
perror("open error");
return fd;
}
while(1){
FD_ZERO(&readfds);
FD_SET(fd,&readfds);
ret = select(fd + 1, &readfds, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (ret == -1){
fprintf(stderr,"select call on%s : an error ocurred",argv[1]);
break;
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&readfds)){
bytesRead = read(fd, &event,sizeof(struct input_event));
if(bytesRead == -1 )
fprintf(stderr,"bytesRead :%ld : an error ocurred",bytesRead);
}
if (event.type == EV_ABS && event.code == ABS_X){
printf("Rotary value is : %d \n",event.value);
}
}
close(fd);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o rotary rotary.c
将编译好的程序使用scp 拷贝到8132 主板上,执行测试,拨动rotary打印如下
CAN应用编程
参考系统下操作CANBUS的方法:CANBUS使用方法,设置can:
ip link set can0 down ip link set can0 type can bitrate 125000 ip link set can0 up ip link set can1 down ip link set can1 type can bitrate 125000 ip link set can1 up
C参考代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <linux/can.h>
#include <linux/can/raw.h>
#include <net/if.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
struct ifreq ifr_recv = {0};
struct ifreq ifr_send = {0};
struct sockaddr_can addr_recv = {0};
struct sockaddr_can addr_send = {0};
struct can_frame frame_recv = {0};
struct can_frame frame_send = {0};
int sockfd_r = -1;
int sockfd_s = -1;
int ret, i;
if ( 3 != argc )
{
fprintf(stderr, "user : %s <can_recv> <can_send>\n", argv[0]);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if ( 0 > (sockfd_r = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW)))
{
perror("socket error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if ( 0 > (sockfd_s = socket(PF_CAN, SOCK_RAW, CAN_RAW)))
{
perror("socket error");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
strcpy(ifr_recv.ifr_name, argv[1]);
ioctl(sockfd_r, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr_recv);
addr_recv.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr_recv.can_ifindex = ifr_recv.ifr_ifindex;
strcpy(ifr_send.ifr_name, argv[2]);
ioctl(sockfd_s, SIOCGIFINDEX, &ifr_send);
addr_send.can_family = AF_CAN;
addr_send.can_ifindex = ifr_send.ifr_ifindex;
ret = bind(sockfd_r, (struct sockaddr *)&addr_recv, sizeof(addr_recv));
if (0 > ret)
{
perror("bind error");
close(sockfd_r);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ret = bind(sockfd_s, (struct sockaddr *)&addr_send, sizeof(addr_send));
if (0 > ret)
{
perror("bind error");
close(sockfd_s);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
setsockopt(sockfd_s, SOL_CAN_RAW, CAN_RAW_FILTER, NULL, 0);
frame_send.data[0] = 0xAA;
frame_send.data[1] = 0xBB;
frame_send.data[2] = 0xCC;
frame_send.data[3] = 0xDD;
frame_send.data[4] = 0xEE;
frame_send.data[5] = 0xFF;
frame_send.data[6] = 0x11;
frame_send.data[7] = 0x22;
frame_send.can_dlc = 8;
frame_send.can_id = 0x123;
while(1)
{
ret = write(sockfd_s, &frame_send, sizeof(frame_send));
if(sizeof(frame_send) != ret)
{
perror("write error");
goto out;
}
printf("%s send :[%d]",ifr_send.ifr_name,frame_send.can_dlc);
for (i = 0; i < frame_send.can_dlc; i++)
printf("%02x ", frame_send.data[i]);
sleep(1);
if (0 > read(sockfd_r, &frame_recv, sizeof(struct can_frame)))
{
perror("read error");
break;
}
if (frame_recv.can_id & CAN_ERR_FLAG)
{
printf("Error frame_recv!\n");
break;
}
printf("\n%s recv :[%d]", ifr_recv.ifr_name,frame_recv.can_dlc);
for (i = 0; i < frame_recv.can_dlc; i++)
printf("%02x ", frame_recv.data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
out:
close(sockfd_r);
close(sockfd_s);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
交叉编译源码:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -o cantest cantest.c
将编译好的程序使用scp 拷贝到主板上,对接CAN0-CAN1执行测试: